Lesson: Writing JavaBeans Components
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Using a BeanInfo
Beans, especially graphic components, can have a dizzying number of properties. If your class inherits from Component, or JComponent, or other Swing classes, it will have over one hundred properties already. Although a builder tool like NetBeans makes it easy to edit bean properties, it can be hard to find the right properties to edit, especially for inexperienced programmers.
Overview of BeanInfo
A BeanInfo is a class that changes how your bean appears in a builder tool. A builder tool can query the BeanInfo to find out which properties it should display first and which should be hidden.
The BeanInfo class for your bean should have the same name as the bean class, with BeanInfo appended. For example, the FaceBean class has a corresponding FaceBeanBeanInfo class that describes it.
Although it is possible to implement a BeanInfo class "by hand," you will find it is much easier to use a tool like NetBeans to edit the BeanInfo.
Creating a BeanInfo in NetBeans
In the Projects pane, Control-click on the name of your bean class and choose BeanInfo Editor... from the context menu.
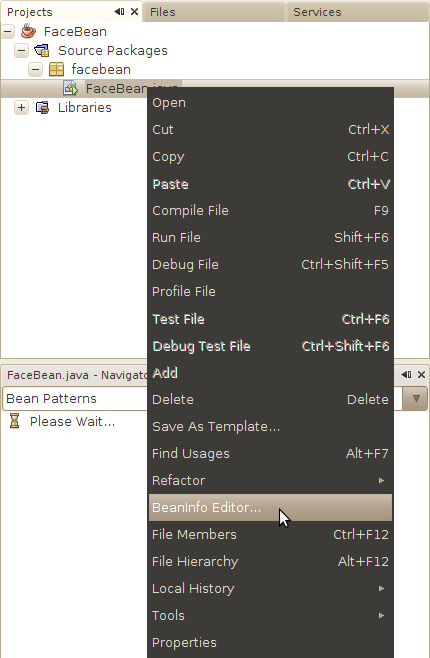
NetBeans notices you don't have a BeanInfo and asks if you want to create one. Click Yes.
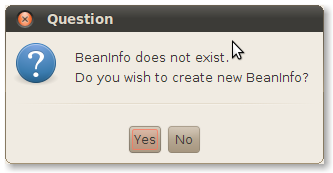
NetBeans creates a new class and drops you into the source code editor. Click on Designer to switch to a visual editor.
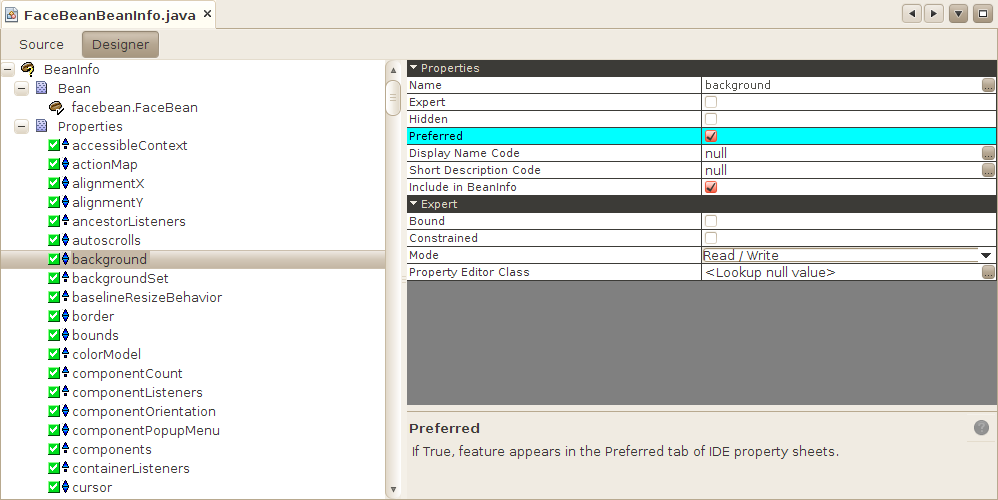
Click for full image
Select properties from the list in the left side of the visual editor, then edit its attributes in the right side. If you don't want a particular property to appear to a developer using a builder tool, click Hidden. To signal that a property should be shown before others, click Preferred. You can also indicate if a property is bound or constrained.
You can provide similar information for the bean's event sources and methods.
When a builder tool loads your bean class to add it to a palette, it will automatically find the corresponding BeanInfo and use it to decide how to present your bean to the developer.