Lesson: Introduction to JAXB
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Customizing JAXB Bindings
The following section describes several examples that build on the concepts demonstrated in the Basic examples.
The goal of this section is to illustrate how to customize JAXB bindings using custom binding declarations, made in one of the following two ways:
- As annotations made inline in an XML schema
- As statements in an external file passed to the JAXB binding compiler
Unlike the examples in Basic JAXB Examples, which focus on the Java code in the respective Main.java class files, the examples here focus on customizations made to the XML schema before generating the schema-derived Java binding classes.
Note: JAXB binding customizations currently must be made by hand. One of the goals of the JAXB technology is to standardize the format of binding declarations, thereby making it possible to create customization tools and to provide a standard interchange format between JAXB implementations.
This section introduces customizations that can be made to JAXB bindings and validation methods. For more information, see JAXB Specification.
Why Customize?
In most cases, the default bindings generated by the JAXB binding compiler are sufficient. There are cases, however, in which you might want to modify the default bindings. Some of these include:
- Creating API documentation for the schema-derived JAXB packages, classes, methods and constants: By adding custom Javadoc tool annotations to your schemas, you can explain concepts, guidelines, and rules specific to your implementation.
- Providing semantically meaningful customized names for cases that the default XML name-to-Java identifier mapping cannot handle automatically; for example:
- To resolve name collisions (as described in Appendix D.2.1 of the JAXB Specification). Note that the JAXB binding compiler detects and reports all name conflicts.
- To provide names for typesafe enumeration constants that are not valid Java identifiers; for example, enumeration over integer values.
- To provide better names for the Java representation of unnamed model groups when they are bound to a Java property or class.
- To provide more meaningful package names than can be derived by default from the target namespace URI.
- Overriding default bindings; for example:
- Specify that a model group must be bound to a class rather than a list.
- Specify that a fixed attribute can be bound to a Java constant.
- Override the specified default binding of XML Schema built-in data types to Java data types. In some cases, you might want to introduce an alternative Java class that can represent additional characteristics of the built-in XML Schema data type.
Customization Overview
This section explains some core JAXB customization concepts:
- Inline and external customizations
- Scope, inheritance, and precedence
- Customization syntax
- Customization namespace prefix
Inline and External Customizations
Customizations to the default JAXB bindings are made in the form of binding declarations passed to the JAXB binding compiler. These binding declarations can be made in either of two ways:
- As inline annotations in a source XML schema
- As declarations in an external binding customizations file
For some, using inline customizations is easier because you can see your customizations in the context of the schema to which they apply. Conversely, using an external binding customization file enables you to customize JAXB bindings without modifying the source schema, and enables you to easily apply customizations to several schema files at once.
Note: You can combine the two types of customizations. For example, you could include a reference to an external binding customizations file in an inline annotation. However, you cannot declare both an inline and external customization on the same schema element.
Each of these types of customization is described in more detail in the following sections:
Inline Customizations
Customizations to JAXB bindings made by means of inline binding declarations in an XML schema file take the form of <xsd:appinfo> elements embedded in schema <xsd:annotation> elements (xsd: is the XML schema namespace prefix, as defined in W3C XML Schema Part 1: Structures). The general form for inline customizations is shown in the following example:
<xs:annotation>
<xs:appinfo>
<!--
...
binding declarations .
...
-->
</xs:appinfo>
</xs:annotation>
Customizations are applied at the location at which they are declared in the schema. For example, a declaration at the level of a particular element applies to that element only. Note that the XML schema namespace prefix must be used with the <annotation> and <appinfo> declaration tags. In the previous example, xs: is used as the namespace prefix, so the declarations are tagged <xs:annotation> and <xs:appinfo>.
External Binding Customization Files
Customizations to JAXB bindings made by using an external file containing binding declarations, take the general form shown in the following example:
<jxb:bindings schemaLocation = "xs:anyURI">
<jxb:bindings node = "xs:string">*
<!-- binding declaration -->
<jxb:bindings>
</jxb:bindings>
- schemaLocation is a URI reference to the remote schema.
- node is an XPath 1.0 expression that identifies the schema node within schemaLocation to which the given binding declaration is associated.
For example, the first schemaLocation/node declaration in a JAXB binding declarations file specifies the schema name and the root schema node:
<jxb:bindings schemaLocation="po.xsd" node="/xs:schema"> </jxb:bindings>
A subsequent schemaLocation/node declaration, such as a simpleType element named ZipCodeType in the previous schema example, takes the following form:
<jxb:bindings node="//xs:simpleType [@name=’ZipCodeType’]">
Binding Customization File Format
Binding customization files must be in ASCII text. The name or extension does not matter; although a typical extension, used in this chapter, is .xjb.
Passing Customization Files to the JAXB Binding Compiler
Customization files containing binding declarations are passed to the JAXB Binding compiler, xjc, using the following syntax:
xjc -b file schema
where file is the name of binding customization file, and schema is the name of the schemas you want to pass to the binding compiler.
You can have a single binding file that contains customizations for multiple schemas, or you can separate the customizations into multiple bindings files; for example:
xjc schema1.xsd schema2.xsd schema3.xsd \
-b bindings123.xjb
xjc schema1.xsd schema2.xsd schema3.xsd \
-b bindings1.xjb \
-b bindings2.xjb \
-b bindings3.xjb
Note that the ordering of schema files and binding files on the command-line does not matter; although each binding customization file must be preceded by its own -b switch on the command line.
For more information about the xjc compiler options in general, see JAXB Compiler Options.
Restrictions for External Binding Customizations
There are several rules that apply to binding declarations made in an external binding customization file that do not apply to similar declarations made inline in a source schema:
- The binding customization file must begin with the
jxb:bindings version attribute, plus attributes for the JAXB and XMLSchema namespaces:
<jxb:bindings version="1.0" xmlns:jxb="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> - The remote schema to which the binding declaration applies
must be identified explicitly in XPath notation by using a
jxb:bindings declaration specifying
schemaLocation and node attributes:
- schemaLocation specifies a URI reference to the remote schema.
- node specifies an XPath 1.0 expression that identifies the schema node within schemaLocation to which the given binding declaration is associated; in the case of the initial jxb:bindings declaration in the binding customization file, this node is typically "/xs:schema".
Similarly, individual nodes within the schema to which customizations are to be applied must be specified using XPath notation; for example:
<jxb:bindings node="//xs:complexType [@name=’USAddress’]">
In such cases, the customization is applied to the node by the binding compiler as if the declaration was embedded inline in the node’s <xs:appinfo> element.
To summarize these rules, the external binding element <jxb:bindings> is only recognized for processing by a JAXB binding compiler in three cases:
- When its parent is an <xs:appinfo> element.
- When it is an ancestor of another <jxb:bindings> element.
- When it is the root element of a document. An XML document that has a <jxb:bindings> element as its root is referred to as an external binding declaration file.
Scope, Inheritance, and Precedence
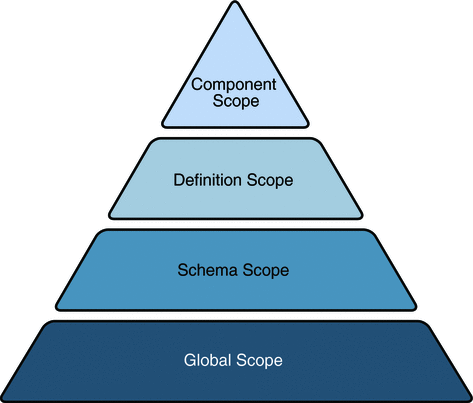
Default JAXB bindings can be customized or overridden at four different levels, or scopes.
The following figure illustrates the inheritance and precedence of customization declarations. Specifically, declarations towards the top of the pyramid inherit and supersede declarations below them.
Component declarations inherit from and supersede Definition declarations; Definition declarations inherit and supersede Schema declarations; and Schema declarations inherit and supersede Global declarations.
Figure: Customization Scope Inheritance and Precedence
Customization Syntax
The syntax for the four types of JAXB binding declarations, the syntax for the XML-to-Java data type binding declarations, and the customization namespace prefix are described in the following section.
- Global Binding Declarations
- Schema Binding Declarations
- Class Binding Declarations
- Property Binding Declarations
- javaType Binding Declarations
- Typesafe Enumeration Binding Declarations
- javadoc Binding Declarations
Global Binding Declarations
Global scope customizations are declared with <globalBindings>. The syntax for global scope customizations is as follows:
<globalBindings>
[ collectionType = "collectionType" ]
[ fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty = "true" | "false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ generateIsSetMethod = "true" | "false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ enableFailFastCheck = "true" | "false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ choiceContentProperty = "true" | "false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ underscoreBinding = "asWordSeparator" | "asCharInWord" ]
[ typesafeEnumBase = "typesafeEnumBase" ]
[ typesafeEnumMemberName = "generateName" | "generateError" ]
[ enableJavaNamingConventions = "true" | "false"
| "1" | "0" ]
[ bindingStyle = "elementBinding" | "modelGroupBinding" ]
[ <javaType> ... </javaType> ]*
</globalBindings>
- collectionType can be either indexed or any fully qualified class name that implements java.util.List.
- fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty can be either true, false, 1, or 0. The default value is false.
- generateIsSetMethod can be either true, false, 1, or 0. The default value is false.
- enableFailFastCheck can be either true, false, 1, or 0. If enableFailFastCheck is true or 1 and the JAXB implementation supports this optional checking, type constraint checking is performed when setting a property. The default value is false. Please note that the JAXB implementation does not support failfast validation.
- choiceContentProperty can be either true, false, 1, or 0. The default value is false. choiceContentProperty is not relevant when the bindingStyle is elementBinding. Therefore, if bindingStyle is specified as elementBinding, then the choiceContentProperty must result in an invalid customization.
- underscoreBinding can be either asWordSeparator or asCharInWord. The default value is asWordSeparator.
- typesafeEnumBase can be a list of QNames, each of which must resolve to a simple type definition. The default value is xs:NCName. See Typesafe Enumeration Binding Declarations for information about the localized mapping of simpleType definitions to Java typesafe enum classes.
- typesafeEnumMemberName can be either generateError or generateName. The default value is generateError.
- enableJavaNamingConventions can be either true, false, 1, or 0. The default value is true.
- bindingStyle can be either elementBinding, or modelGroupBinding. The default value is elementBinding.
- <javaType> can be zero or more javaType binding declarations. For more information, see javaType Binding Declarations.
<globalBindings> declarations are only valid in the annotation element of the top-level schema element. There can only be a single instance of a <globalBindings> declaration in any given schema or binding declarations file. If one source schema includes or imports a second source schema, the <globalBindings> declaration must be declared in the first source schema.
Schema Binding Declarations
Schema scope customizations are declared with <schemaBindings>. The syntax for schema scope customizations is:
<schemaBindings>
[ <package> package </package> ]
[ <nameXmlTransform> ... </nameXmlTransform> ]*
</schemaBindings>
<package
[ name = "packageName" ]
[ <javadoc> ... </javadoc> ]
</package>
<nameXmlTransform>
[ <typeName
[ suffix="suffix" ]
[ prefix="prefix" ] /> ]
[ <elementName
[ suffix="suffix" ]
[ prefix="prefix" ] /> ]
[ <modelGroupName
[ suffix="suffix" ]
[ prefix="prefix" ] /> ]
[ <anonymousTypeName
[ suffix="suffix" ]
[ prefix="prefix" ] /> ]
</nameXmlTransform>
As shown above, <schemaBinding> declarations include two subcomponents:
- <package>...</package> specifies the name of the package and, if desired, the location of the API documentation for the schema-derived classes.
- <nameXmlTransform>...</nameXmlTransform> specifies customizations to be applied.
Class Binding Declarations
The <class> binding declaration enables you to customize the binding of a schema element to a Java content interface or a Java Element interface. <class> declarations can be used to customize:
- A name for a schema-derived Java interface
- An implementation class for a schema-derived Java content interface
The syntax for <class> customizations is:
<class
[ name = "className"]
[ implClass= "implClass" ] >
[ <javadoc> ... </javadoc> ]
</class>
- name is the name of the derived Java interface. It must be a valid Java interface name and must not contain a package prefix. The package prefix is inherited from the current value of the package.
- implClass is the name of the implementation class for className and must include the complete package name.
- The <javadoc> element specifies the Javadoc tool annotations for the schema-derived Java interface. The string entered here must use CDATA or < to escape embedded HTML tags.
Property Binding Declarations
The <property> binding declaration enables you to customize the binding of an XML schema element to its Java representation as a property. The scope of customization can either be at the definition level or component level depending upon where the <property> binding declaration is specified.
The syntax for <property> customizations is:
<property
[ name = "propertyName"]
[ collectionType = "propertyCollectionType" ]
[ fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty = "true" |
"false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ generateIsSetMethod = "true" |
"false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ enableFailFastCheck ="true" |
"false" | "1" | "0" ]
[ <baseType> ... </baseType> ]
[ <javadoc> ... </javadoc> ]
</property>
<baseType>
<javaType> ... </javaType>
</baseType>
- name defines the customization value propertyName; it must be a valid Java identifier.
- collectionType defines the customization value propertyCollectionType, which is the collection type for the property, propertyCollectionType. If specified, the property can be either indexed or any fully-qualified class name that implements java.util.List.
- fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty defines the customization value fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty. The value can be either true, false, 1, or 0.
- generateIsSetMethod defines the customization value of generateIsSetMethod. The value can be either true, false, 1, or 0.
- enableFailFastCheck defines the customization value enableFailFastCheck. The value can be either true, false, 1, or 0. Please note that the JAXB implementation does not support failfast validation.
- <javadoc> customizes the Javadoc tool annotations for the property’s getter method.
javaType Binding Declarations
The <javaType> declaration provides a way to customize the translation of XML data types to and from Java data types. XML provides more data types than Java, so the <javaType> declaration enables you to specify custom data type bindings when the default JAXB binding cannot sufficiently represent your schema.
The target Java data type can be a Java built-in data type or an application-specific Java data type. If an application-specific Java data type is used as the target, your implementation must also provide parse and print methods for unmarshalling and marshalling data. To this end, the JAXB specification supports a parseMethod and printMethod:
- The parseMethod is called during unmarshalling to convert a string from the input document into a value of the target Java data type.
- The printMethod is called during marshalling to convert a value of the target type into a lexical representation.
If you prefer to define your own data type conversions, JAXB defines a static class, DatatypeConverter, to assist in the parsing and printing of valid lexical representations of the XML Schema built-in data types.
The syntax for the <javaType> customization is:
<javaType name= "javaType"
[ xmlType= "xmlType" ]
[ hasNsContext = "true" | "false" ]
[ parseMethod= "parseMethod" ]
[ printMethod= "printMethod" ]>
- name is the Java data type to which xmlType is to be bound.
- xmlType is the name of the XML Schema data type to which javaType is to be bound; this attribute is required when the parent of the <javaType> declaration is <globalBindings>.
- hasNsContext allows a namespace context to be specified as a second parameter to a print or a parse method; can be either true, false, 1, or 0. By default, this attribute is false, and in most cases, there is no need to change it.
- parseMethod is the name of the parse method to be called during unmarshalling.
- printMethod is the name of the print method to be called during marshalling.
The <javaType> declaration can be used in:
- A <globalBindings> declaration
- An annotation element for simple type definitions, GlobalBindings, and <basetype> declarations
- A <property> declaration
See MyDatatypeConverter Class for an example of how <javaType> declarations and the DatatypeConverterInterface interface are implemented in a custom data type converter class.
Typesafe Enumeration Binding Declarations
The typesafe enumeration declarations provide a localized way to map XML simpleType elements to Java typesafe enum classes. There are two types of typesafe enumeration declarations you can make:
- <typesafeEnumClass> lets you map an entire simpleType class to typesafe enum classes.
- <typesafeEnumMember> lets you map just selected members of a simpleType class to typesafe enum classes.
In both cases, there are two primary limitations on this type of customization:
- Only simpleType definitions with enumeration facets can be customized using this binding declaration.
- This customization only applies to a single simpleType definition at a time. To map sets of similar simpleType definitions on a global level, use the typesafeEnumBase attribute in a <globalBindings> declaration, as described in Global Binding Declarations.
The syntax for the <typesafeEnumClass> customization is:
<typesafeEnumClass
[ name = "enumClassName" ]
[ <typesafeEnumMember> ... </typesafeEnumMember> ]*
[ <javadoc> enumClassJavadoc </javadoc> ]
</typesafeEnumClass>
- name must be a valid Java Identifier, and must not have a package prefix.
- You can have zero or more <typesafeEnumMember> declarations embedded in a <typesafeEnumClass> declaration.
- <javadoc> customizes the Javadoc tool annotations for the enumeration class.
The syntax for the <typesafeEnumMember> customization is:
<typesafeEnumMember
name = "enumMemberName">
[ value = "enumMemberValue" ]
[ <javadoc> enumMemberJavadoc </javadoc> ]
</typesafeEnumMember>
- name must always be specified and must be a valid Java identifier.
- value must be the enumeration value specified in the source schema.
- <javadoc> customizes the Javadoc tool annotations for the enumeration constant.
For inline annotations, the <typesafeEnumClass> declaration must be specified in the annotation element of the <simpleType> element. The <typesafeEnumMember> must be specified in the annotation element of the enumeration member. This enables the enumeration member to be customized independently from the enumeration class.
For information about typesafe enum design patterns, see the sample chapter of Joshua Bloch’s Effective Java Programming on the Oracle Technology Network..
javadoc Binding Declarations
The <javadoc> declaration lets you add custom Javadoc tool annotations to schema-derived JAXB packages, classes, interfaces, methods, and fields. Note that <javadoc> declarations cannot be applied globally; they are only valid as sub-elements of other binding customizations.
The syntax for the <javadoc> customization is:
<javadoc>
Contents in <b>Javadoc<\b> format.
</javadoc>
or
<javadoc>
<<![CDATA[Contents in <b>Javadoc<\b> format ]]>
</javadoc>
Note that documentation strings in <javadoc> declarations applied at the package level must contain <body> open and close tags; for example:
<jxb:package
name="primer.myPo">
<jxb:javadoc>
<![CDATA[<body>
Package level documentation for generated package primer.myPo.
</body>]]>
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:package>
Customization Namespace Prefix
All standard JAXB binding declarations must be preceded by a namespace prefix that maps to the JAXB namespace URI http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb. For example, in this sample, jxb: is used. To this end, any schema you want to customize with standard JAXB binding declarations must include the JAXB namespace declaration and JAXB version number at the top of the schema file. For example, in po.xsd for the Customize Inline example, the namespace declaration is as follows:
<xsd:schema
xmlns:xsd= "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:jxb= "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb"
jxb:version="1.0">
A binding declaration with the jxb namespace prefix takes the following form:
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:globalBindings
binding declarations />
<jxb:schemaBindings>
...
binding declarations .
...
</jxb:schemaBindings>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
Note that in this example, the globalBindings and schemaBindings declarations are used to specify, respectively, global scope and schema scope customizations. These customization scopes are described in more detail in Scope, Inheritance, and Precedence.
Customize Inline Example
The Customize Inline example illustrates some basic customizations made by means of inline annotations to an XML schema named po.xsd. In addition, this example implements a custom data type converter class, MyDatatypeConverter.java, which illustrates print and parse methods in the <javaType> customization for handling custom data type conversions.
To summarize this example:
- po.xsd is an XML schema containing inline binding customizations.
- MyDatatypeConverter.java is a Java class file that implements print and parse methods specified by <javaType> customizations in po.xsd.
- Main.java is the primary class file in the Customize Inline example, which uses the schema-derived classes generated by the JAXB compiler.
Building and Running the Customize Inline Example Using Ant
To compile and run the Customize Inline example using Ant, in a terminal window, go to the jaxb-ri-install/samples/inline-customize/ directory and type the following:
ant
Key customizations in this sample and the custom MyDatatypeConverter.java class are described in more detail in the following section.
Customized Schema
The customized schema used in the Customize Inline example is in the file jaxb-ri-install/samples/inline-customize/po.xsd. The customizations are in the <xsd:annotation> tags.
Global Binding Declarations
The following code example shows the globalBindings declarations in po.xsd:
<jxb:globalBindings
fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty="true"
collectionType="java.util.Vector"
typesafeEnumBase="xsd:NCName"
choiceContentProperty="false"
typesafeEnumMemberName="generateError"
bindingStyle="elementBinding"
enableFailFastCheck="false"
generateIsSetMethod="false"
underscoreBinding="asCharInWord"/>
In this example, all values are set to the defaults except for collectionType.
- Setting fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty to true indicates that all fixed attributes should be bound to Java constants. By default, fixed attributes are mapped to either a simple or a collection property, whichever is more appropriate.
- Setting collectionType to java.util.Vector specifies that all lists in the generated implementation classes are represented internally as vectors. Note that the class name you specify for collectionType must implement java.util.List and be callable by newInstance.
- If typesafeEnumBase is set to xsd:string, it is a global way to specify that all simple type definitions derived directly or indirectly from xsd:string and having enumeration facets, must be bound by default to a typesafe enum. If typesafeEnumBase is set to an empty string (""), no simple type definitions are bound to a typesafe enum class by default. The value of typesafeEnumBase can be any atomic simple type definition except xsd:boolean and both binary types.
- The JAXB implementation does not support the
enableFailFastCheck attribute.
Note: Using typesafe enum classes enables you to map schema enumeration values to Java constants, which makes it possible to do comparisons on Java constants rather than on string values.
Schema Binding Declarations
The following code shows the schema binding declarations in po.xsd:
<jxb:schemaBindings>
<jxb:package name="primer.myPo">
<jxb:javadoc>
<![CDATA[<body>
Package level documentation for generated package primer.myPo.
</body>]]>
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:package>
<jxb:nameXmlTransform>
<jxb:elementName suffix="Element"/>
</jxb:nameXmlTransform>
</jxb:schemaBindings>
- <jxb:package name="primer.myPo"/> specifies the primer.myPo as the package in which the schema-derived classes are generated.
- <jxb:nameXmlTransform> specifies that all generated Java element interfaces have Element appended to the generated names by default. For example, when the JAXB compiler is run against this schema, the element interfaces CommentElement and PurchaseOrderElement are generated. By contrast, without this customization, the default binding generates Comment and PurchaseOrder. This customization is useful if a schema uses the same name in different symbol spaces; for example, in the global element and type definitions. In such cases, this customization enables you to resolve the collision with one declaration rather than having to individually resolve each collision with a separate binding declaration.
- <jxb:javadoc> specifies customized Javadoc tool annotations for the primer.myPo package. Note that, unlike the <javadoc> declarations at the class level, as shown in the following example, the opening and closing <body> tags must be included when the <javadoc> declaration is made at the package level.
Class Binding Declarations
The following code shows the class binding declarations in po.xsd:
<xsd:complexType name="PurchaseOrderType">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:class name="POType">
<jxb:javadoc>
A <b>Purchase Order</b>
consists of addresses and items.
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:class>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<!-- ... -->
</xsd:complexType>
The Javadoc tool annotations for the schema-derived POType class will contain the description "A <b>Purchase Order</b> consists of addresses and items." The < is used to escape the opening bracket on the <b> HTML tags.
Note: When a <class> customization is specified in the appinfo element of a complexType definition, as shown in the previous example, the complexType definition is bound to a Java content interface.
Later in po.xsd, another <javadoc> customization is declared at this class level, but this time the HTML string is escaped with CDATA:
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:class>
<jxb:javadoc>
<![CDATA[
First line of documentation for a
<b>USAddress</b>.]]>
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:class>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
Note: If you want to include HTML tags in a <jaxb:javadoc> customization, you must enclose the data within a CDATA section or escape all left angle brackets using <. See XML 1.0 2nd Edition for more information.
Property Binding Declarations
Of particular interest here is the generateIsSetMethod customization, which causes two additional property methods, isSetQuantity and unsetQuantity, to be generated. These methods enable a client application to distinguish between schema default values and values occurring explicitly within an instance document.
For example, in po.xsd:
<xsd:complexType name="Items">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="item"
minOccurs="1"
maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element
name="productName"
type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element
name="quantity"
default="10">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:property
generateIsSetMethod="true"/>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<!-- ... -->
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
The @generateIsSetMethod applies to the quantity element, which is bound to a property within the Items.ItemType interface. unsetQuantity and isSetQuantity methods are generated in the Items.ItemType interface.
MyDatatypeConverter Class
The class jaxb-ri-install/samples/inline-customize/src/inlinecustomize/primer/MyDatatypeConverter, shown in the following example, provides a way to customize the translation of XML data types to and from Java data types using a <javaType> customization.
package primer;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter;
public class MyDatatypeConverter {
public static short parseIntegerToShort(String value) {
BigInteger result = DatatypeConverter.parseInteger(value);
return (short)(result.intValue());
}
public static String printShortToInteger(short value) {
BigInteger result = BigInteger.valueOf(value);
return DatatypeConverter.printInteger(result);
}
public static int parseIntegerToInt(String value) {
BigInteger result = DatatypeConverter.parseInteger(value);
return result.intValue();
}
public static String printIntToInteger(int value) {
BigInteger result = BigInteger.valueOf(value);
return DatatypeConverter.printInteger(result);
}
};
The following code shows how the MyDatatypeConverter class is referenced in a <javaType> declaration in po.xsd:
<xsd:simpleType name="ZipCodeType">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:javaType name="int"
parseMethod="primer.MyDatatypeConverter.parseIntegerToInt"
printMethod="primer.MyDatatypeConverter.printIntTo Integer" />
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:integer">
<xsd:minInclusive value="10000"/>
<xsd:maxInclusive value="99999"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
In this example, the jxb:javaType binding declaration overrides the default JAXB binding of this type to java.math.BigInteger. For the purposes of the Customize Inline example, the restrictions on ZipCodeType (specifically, that valid United States ZIP codes are limited to five digits) make it possible that all valid values can fit within the Java primitive data type int. Note also that, because <jxb:javaType name="int"/> is declared within ZipCodeType, the customization applies to all JAXB properties that reference this simpleType definition, including the getZip and setZip methods.
DataType Converter Example
The DataType Converter example is similar to the Customize Inline example. As with the Customize Inline example, the customizations in the Datatype Converter example are made by using inline binding declarations in the XML schema for the application, po.xsd.
The global, schema, and package, and most of the class customizations for the Customize Inline and DataType Converter examples are identical. Where the Datatype Converter example differs from the Customize Inline example is in the parseMethod and printMethod used for converting XML data to the Java int data type.
Specifically, rather than using methods in the custom MyDataTypeConverter class to perform these data type conversions, the Datatype Converter example uses the built-in methods provided by javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter:
<xsd:simpleType name="ZipCodeType">
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:javaType
name="int"
parseMethod="javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter.parseInt"
printMethod="javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter.printInt"/>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:integer">
<xsd:minInclusive value="10000"/>
<xsd:maxInclusive value="99999"/>
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
Building and Running the Datatype Converter Example Using Ant
To compile and run the DataType Converter example using Ant, in a terminal window, go to the jaxb-ri-install/samples/datatypeconverter/ directory and type the following:
ant
Binding Declaration Files
The following sections provide information about binding declaration files:
- JAXB Version, Namespace, and Schema Attributes
- Global and Schema Binding Declarations
- Class Declarations
JAXB Version, Namespace, and Schema Attributes
All JAXB binding declaration files must begin with:
- JAXB version number
- Namespace declarations
- Schema name and node
The version, namespace, and schema declarations in bindings.xjb are as follows:
<jxb:bindings
version="1.0"
xmlns:jxb="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<jxb:bindings
schemaLocation="po.xsd"
node="/xs:schema">
<!-- ...
binding-declarations
... -->
</jxb:bindings>
<!--
schemaLocation="po.xsd"
node="/xs:schema" -->
</jxb:bindings>
JAXB Version Number
An XML file with a root element of <jaxb:bindings> is considered an external binding file. The root element must specify the JAXB version attribute with which its binding declarations must comply; specifically the root <jxb:bindings> element must contain either a <jxb:version> declaration or a version attribute. By contrast, when making binding declarations inline, the JAXB version number is made as an attribute of the <xsd:schema> declaration:
<xsd:schema
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:jxb="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/jaxb"
jxb:version="1.0">
Namespace Declarations
As shown in JAXB Version, Namespace, and Schema Attributes, the namespace declarations in the external binding declarations file include both the JAXB namespace and the XMLSchema namespace. Note that the prefixes used in this example could in fact be anything you want; the important thing is to consistently use whatever prefixes you define here in subsequent declarations in the file.
Schema Name and Schema Node
The fourth line of the code in JAXB Version, Namespace, and Schema Attributes specifies the name of the schema to which this binding declarations file applies, and the schema node at which the customizations will first take effect. Subsequent binding declarations in this file can reference specific nodes within the schema, but this first declaration should encompass the schema as a whole; for example, in bindings.xjb:
<jxb:bindings schemaLocation="po.xsd" node="/xs:schema">
Global and Schema Binding Declarations
The global schema binding declarations in bindings.xjb are the same as those in po.xsd for the DataType Converter example. The only difference is that because the declarations in po.xsd are made inline, you must embed them in <xs:appinfo> elements, which are in turn embedded in <xs:annotation> elements. Embedding declarations in this way is unnecessary in the external bindings file.
<jxb:globalBindings
fixedAttributeAsConstantProperty="true"
collectionType="java.util.Vector"
typesafeEnumBase="xs:NCName"
choiceContentProperty="false"
typesafeEnumMemberName="generateError"
bindingStyle="elementBinding"
enableFailFastCheck="false"
generateIsSetMethod="false"
underscoreBinding="asCharInWord"/>
<jxb:schemaBindings>
<jxb:package name="primer.myPo">
<jxb:javadoc>
<![CDATA[<body>
Package level documentation for generated package
primer.myPo.</body>]]>
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:package>
<jxb:nameXmlTransform>
<jxb:elementName suffix="Element"/>
</jxb:nameXmlTransform>
</jxb:schemaBindings>
By comparison, the syntax used in po.xsd for the DataType Converter example is:
<xsd:annotation>
<xsd:appinfo>
<jxb:globalBindings
...
binding-declarations
...
<jxb:schemaBindings>
...
binding-declarations
...
</jxb:schemaBindings>
</xsd:appinfo>
</xsd:annotation>
Class Declarations
The class-level binding declarations in bindings.xjb differ from the analogous declarations in po.xsd for the Datatype Converter example in two ways:
- As with all other binding declarations in bindings.xjb, you do not need to embed your customizations in schema <xsd:appinfo> elements.
- You must specify the schema node to which the customization is applied. The general syntax for this type of declaration is:
<jxb:bindings node="//node-type[@name=’node-name’]">
For example, the following code shows binding declarations for the complexType named USAddress.
<jxb:bindings node="//xs:complexType [@name=’USAddress’]">
<jxb:class>
<jxb:javadoc>
<![CDATA[
First line of documentation for a <b>USAddress</b>.
]]>
</jxb:javadoc>
</jxb:class>
<jxb:bindings node=".//xs:element [@name=’name’]">
<jxb:property name="toName"/>
</jxb:bindings>
<jxb:bindings node=".//xs:element [@name=’zip’]">
<jxb:property name="zipCode"/>
</jxb:bindings>
</jxb:bindings>
<!--
node="//xs:complexType
[@name=’USAddress’]" -->
Note in this example that USAddress is the parent of the child elements name and zip, and therefore a </jxb:bindings> tag encloses the bindings declarations for the child elements and the class-level javadoc declaration.
External Customize Example
The External Customize example is identical to the DataType Converter example, except that the binding declarations in the External Customize example are made by using an external binding declarations file rather than inline in the source XML schema.
The binding customization file used in the External Customize example is jaxb-ri-install/samples/external-customize/binding.xjb.
This section compares the customization declarations in bindings.xjb with the analogous declarations used in the XML schema, po.xsd, in the DataType Converter example. The two sets of declarations achieve precisely the same results.
Building and Running the External Customize Example Using Ant
To compile and run the External Customize example using Ant, in a terminal window, go to the jaxb-ri-install/samples/external-customize/ directory and type the following:
ant