Lesson: JDBC Basics
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Using JDBC with GUI API
The sample
CoffeesFrame.java demonstrates how to integrate JDBC with a GUI API, in particular, the Swing API. It displays the contents of the COFFEES database table in a table and contains fields and buttons that enable you to add rows to the table. The following is a screenshot of this sample:
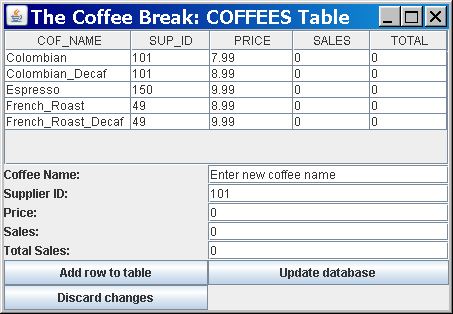
The sample contains five text fields that correspond to each of the columns in the COFFEES table. It also contains three buttons:
- Add row to table: Adds a row to the sample's table based on the data entered in the text fields.
- Update database: Updates the table
COFFEESbased on the data in the sample's table. - Discard changes: Retrieves the contents of the
COFFEEStable, replacing the existing data in the sample's table.
This sample (which requires
CoffeesTableModel.java) demonstrates the following general steps to integrate JDBC with the Swing API:
- Implementing the
TableModelinterface - Implementing the
RowSetListenerinterface - Laying out the Swing components
- Adding listeners for the buttons in the sample
Implementing javax.swing.event.TableModel
The TableModel interface enables a Java Swing application to manage data in a JTable object. The sample,
CoffeesTableModel.java, implements this interface. It specifies how a JTable object should retrieve data from a RowSet object and display it in a table.
Note: Although this sample displays the contents of the COFFEES table in a Swing application, the class CoffeesTableModel should work for any SQL table provided that its data can be represented with String objects. (However, the fields that enable users to add rows to COFFEES, which are specified in the class CoffeesFrame, would have to be modified for other SQL tables.)
Before implementing the methods of the interface TableModel, the constructor of the class CoffeeTableModel initializes various member variables required for these implemented methods as follows:
public CoffeesTableModel(CachedRowSet rowSetArg)
throws SQLException {
this.coffeesRowSet = rowSetArg;
this.metadata = this.coffeesRowSet.getMetaData();
numcols = metadata.getColumnCount();
// Retrieve the number of rows.
this.coffeesRowSet.beforeFirst();
this.numrows = 0;
while (this.coffeesRowSet.next()) {
this.numrows++;
}
this.coffeesRowSet.beforeFirst();
}
The following describes the member variables initialized in this constructor:
-
CachedRowSet coffeesRowSet: Stores the contents of the tableCOFFEES.This sample uses a
RowSetobject, in particular, aCachedRowSetobject, rather than aResultSetobject for two reasons. ACachedRowSetobject enables the user of the application to make changes to the data contained in it without being connected to the database. In addition, because aCachedRowSetobject is a JavaBeans component, it can notify other components when certain things happen to it. In this sample, when a new row is added to theCachedRowSetobject, it notifies the Swing component that is rendering its data in a table to refresh itself and display the new row. -
ResultSetMetaData metadata: Retrieves the number of columns in the tableCOFFEESas well as the names of each of them. -
int numcols, numrows: Stores the number of columns and rows, respectively, in the tableCOFFEES.
The CoffeesTableModel.java sample implements the following methods from TableModel interface:
Class<?> getColumnClass(int columnIndex): Returns the most specific superclass for all the cell values in the column.int getColumnCount(): Returns the number of columns in the model.String getColumnName(int columnIndex): Returns the name of the column specified by the parametercolumnIndex.int getRowCount(): Returns the number of rows in the model.Object getValueAt(int rowIndex, int columnIndex): Returns the value for the cell at intersection of the columncolumnIndexand the rowrowIndex.boolean isCellEditable(int rowIndex, int columnIndex): Returns true if the cell at the intersection of the columnrowIndexand the rowcolumnIndexcan be edited.
The following methods have not been implemented because this sample does not allow users to directly edit the contents of the table:
void addTableModelListener(TableModelListener l): Adds a listener to the list that is notified each time a change to the data model occurs.void removeTableModelListener(TableModelListener l): Removes a listener from the list that is notified each time a change to the data model occurs.void setValueAt(Object aValue, int rowIndex, int columnIndex): Sets the value in the cell at the intersection of the columncolumnIndexand the rowrowIndexto the objectaValue.
Implementing getColumnCount and getRowCount
The methods getColumnCount and getRowCount return the value of the member variables numcols and numrows, respectively:
public int getColumnCount() {
return numcols;
}
public int getRowCount() {
return numrows;
}
Implementing getColumnClass
The getColumnClass method returns the data type of the specified column. To keep things simple, this method returns the String class, thereby converting all data in the table into String objects. The JTable class uses this method to determine how to render data in the GUI application.
public Class getColumnClass(int column) {
return String.class;
}
Implementing getColumnName
The getColumnName method returns the name of the specified column. The JTable class uses this method to label each of its columns.
public String getColumnName(int column) {
try {
return this.metadata.getColumnLabel(column + 1);
} catch (SQLException e) {
return e.toString();
}
}
Implementing getColumnAt
The getColumnAt method retrieves the value at the specified row and column in the row set coffeesRowSet. The JTable class uses this method to populate its table. Note that SQL starts numbering its rows and columns at 1, but the TableModel interface starts at 0; this is the reason why the rowIndex and columnIndex values are incremented by 1.
public Object getValueAt(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
try {
this.coffeesRowSet.absolute(rowIndex + 1);
Object o = this.coffeesRowSet.getObject(columnIndex + 1);
if (o == null)
return null;
else
return o.toString();
} catch (SQLException e) {
return e.toString();
}
}
Implementing isCellEditable
Because this sample does not allow users to directly edit the contents of the table (rows are added by another window control), this method returns false regardless of the values of rowIndex and columnIndex:
public boolean isCellEditable(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
return false;
}
Implementing javax.sql.RowSetListener
The class CoffeesFrame implements only one method from the interface RowSetListener, rowChanged. This method is called when a user adds a row to the table.
public void rowChanged(RowSetEvent event) {
CachedRowSet currentRowSet =
this.myCoffeesTableModel.coffeesRowSet;
try {
currentRowSet.moveToCurrentRow();
myCoffeesTableModel = new CoffeesTableModel(
myCoffeesTableModel.getCoffeesRowSet());
table.setModel(myCoffeesTableModel);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
JDBCTutorialUtilities.printSQLException(ex);
// Display the error in a dialog box.
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
CoffeesFrame.this,
new String[] {
// Display a 2-line message
ex.getClass().getName() + ": ",
ex.getMessage()
}
);
}
}
This method updates the table in the GUI application.
Laying Out Swing Components
The constructor of the class CoffeesFrame initializes and lays out the Swing components. The following statement retrieves the contents of the COFFEES table, stores the contents in the CachedRowSet object myCachedRowSet, and initializes the JTable Swing component:
CachedRowSet myCachedRowSet = getContentsOfCoffeesTable(); myCoffeesTableModel = new CoffeesTableModel(myCachedRowSet); myCoffeesTableModel.addEventHandlersToRowSet(this); // Displays the table table = new JTable(); table.setModel(myCoffeesTableModel);
As mentioned previously, instead of a ResultSet object to represent the contents of the COFFEES table, this sample uses a RowSet object, notably a CachedRowSet object.
The method CoffeesFrame.getContentsOfCoffeesTable retrieves the contents of the table COFFEES.
The method CoffeesTableModel.addEventHandlersToRowSet adds the event handler defined in the CoffeesFrame class, which is the method rowChanged, to the row set member variable CoffeesTableModel.coffeesRowSet. This enables the class CoffeesFrame to notify the row set coffeesRowSet of any events, in particular, when a user clicks the button Add row to table, Update database, or Discard changes. When the row set coffeesRowSet is notified of one of these changes, the method CoffeesFrame.rowChanged is called.
The statement table.setModel(myCoffeesTableModel) specifies that it use the CoffeesTableModel object myCoffeesTableModel to populate the JTable Swing component table.
The following statements specify that the CoffeesFrame class use the layout GridBagLayout to lay out its Swing components:
Container contentPane = getContentPane();
contentPane.setComponentOrientation(
ComponentOrientation.LEFT_TO_RIGHT);
contentPane.setLayout(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints();
See
How to Use GridBagLayout in the
Creating a GUI With JFC/Swing for more information about using the layout GridBagLayout.
See the source code for
CoffeesFrame.java to see how the Swing components of this sample are added to the layout GridBagLayout.
Adding Listeners for Buttons
The following statement adds a listener to the button Add row to table:
button_ADD_ROW.addActionListener(
new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(
CoffeesFrame.this, new String[] {
"Adding the following row:",
"Coffee name: [" +
textField_COF_NAME.getText() +
"]",
"Supplier ID: [" +
textField_SUP_ID.getText() + "]",
"Price: [" +
textField_PRICE.getText() + "]",
"Sales: [" +
textField_SALES.getText() + "]",
"Total: [" +
textField_TOTAL.getText() + "]"
}
);
try {
myCoffeesTableModel.insertRow(
textField_COF_NAME.getText(),
Integer.parseInt(textField_SUP_ID.getText().trim()),
Float.parseFloat(textField_PRICE.getText().trim()),
Integer.parseInt(textField_SALES.getText().trim()),
Integer.parseInt(textField_TOTAL.getText().trim())
);
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
displaySQLExceptionDialog(sqle);
}
}
});
When a user clicks this button, it performs the following:
- Creates a message dialog box that displays the row to be added to the table.
- Calls the method
CoffeesTableModel.insertRow, which adds the row to the member variableCoffeesTableModel.coffeesRowSet.
If an SQLException is thrown, then the method CoffeesFrame.displaySQLExceptionDialog creates a message dialog box that displays the content of the SQLException.
The following statement adds a listener to the button Update database:
button_UPDATE_DATABASE.addActionListener(
new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
myCoffeesTableModel.coffeesRowSet.acceptChanges();
msgline.setText("Updated database");
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
displaySQLExceptionDialog(sqle);
// Now revert back changes
try {
createNewTableModel();
msgline.setText("Discarded changes");
} catch (SQLException sqle2) {
displaySQLExceptionDialog(sqle2);
}
}
}
}
);
When a user clicks this button, the table COFFEES is updated with the contents of the row set myCoffeesTableModel.coffeesRowSet.
The following statement adds a listener to the button Discard changes:
button_DISCARD_CHANGES.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
createNewTableModel();
} catch (SQLException sqle) {
displaySQLExceptionDialog(sqle);
}
}
});
When a user clicks this button, the method CoffeesFrame.createNewTableModel is called, which repopulates the JTable component with the contents of the COFFEES table.