Lesson: Naming and Directory Operations
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Lookup an Object
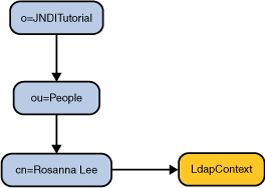
To look up an object from the naming service, use Context.lookup() and pass it the name of the object that you want to retrieve. Suppose that there is an object in the naming service with the name cn=Rosanna Lee,ou=People. To retrieve the object, you would write
Object obj = ctx.lookup("cn=Rosanna Lee,ou=People");
The type of object that is returned by lookup() depends both on the underlying naming system and on the data associated with the object itself. A naming system can contain many different types of objects, and a lookup of an object in different parts of the system might yield objects of different types. In this example, "cn=Rosanna Lee,ou=People" happens to be bound to a context object (javax.naming.ldap.LdapContext). You can cast the result of lookup() to its target class.
For example, the following code looks up the object "cn=Rosanna Lee,ou=People" and casts it to LdapContext.
import javax.naming.ldap.LdapContext;
...
LdapContext ctx = (LdapContext) ctx.lookup("cn=Rosanna Lee,ou=People");
The complete example is in the file
Lookup.java.
There are two new static methods available in Java SE 6 to lookup a name:
These methods provide a shortcut way of looking up a name without instantiating an InitialContext.