Lesson: Advanced Topics in Java2D
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Constructing Complex Shapes from Geometry Primitives
Constructive area geometry (CAG) is the process of creating new geometric shapes by performing boolean operations on existing ones. In the Java 2D API the
Area class implements the
Shape interface and supports the following boolean operations.
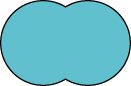 |
Union |
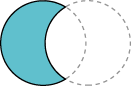 |
Subtraction |
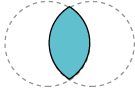 |
Intersection |
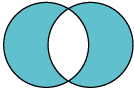 |
Exclusive-or (XOR) |
Example: Areas
In this example Area objects construct a pear shape from several ellipses.
Note: If you don't see the applet running, you need to install at least the Java SE Development Kit (JDK) 7 release.
Pear.java
The leaves are each created by performing an intersection on two overlapping circles.
leaf = new Ellipse2D.Double(); ... leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf2 = new Area(leaf); ... leaf.setFrame(ew-16, eh-29, 15.0, 15.0); leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf.setFrame(ew-14, eh-47, 30.0, 30.0); leaf2 = new Area(leaf); leaf1.intersect(leaf2); g2.fill(leaf1); ... leaf.setFrame(ew+1, eh-29, 15.0, 15.0); leaf1 = new Area(leaf); leaf2.intersect(leaf1); g2.fill(leaf2);
Overlapping circles are also used to construct the stem through a subtraction operation.
stem = new Ellipse2D.Double(); ... stem.setFrame(ew, eh-42, 40.0, 40.0); st1 = new Area(stem); stem.setFrame(ew+3, eh-47, 50.0, 50.0); st2 = new Area(stem); st1.subtract(st2); g2.fill(st1);
The body of the pear is constructed by performing a union operation on a circle and an oval.
circle = new Ellipse2D.Double(); oval = new Ellipse2D.Double(); circ = new Area(circle); ov = new Area(oval); ... circle.setFrame(ew-25, eh, 50.0, 50.0); oval.setFrame(ew-19, eh-20, 40.0, 70.0); circ = new Area(circle); ov = new Area(oval); circ.add(ov); g2.fill(circ);