Lesson: Advanced Topics in Java2D
The Java Tutorials have been written for JDK 8. Examples and practices described in this page don't take advantage of improvements introduced in later releases and might use technology no longer available.
See Java Language Changes for a summary of updated language features in Java SE 9 and subsequent releases.
See JDK Release Notes for information about new features, enhancements, and removed or deprecated options for all JDK releases.
Compositing Graphics
The
AlphaComposite class encapsulates various compositing styles, which determine how overlapping objects are rendered. An AlphaComposite can also have an alpha value that specifies the degree of transparency: alpha = 1.0 is totally opaque, alpha = 0.0 totally transparent (clear). AlphaComposite supports most of the standard Porter-Duff compositing rules shown in the following table.
| Compositing Rule | Description |
|---|---|
Source-over (SRC_OVER)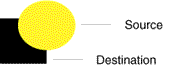 |
If pixels in the object being rendered (the source) have the same location as previously rendered pixels (the destination), the source pixels are rendered over the destination pixels. |
Source-in (SRC_IN) |
If pixels in the source and the destination overlap, only the source pixels in the overlapping area are rendered. |
Source-out (SRC_OUT) |
If pixels in the source and the destination overlap, only the source pixels outside of the overlapping area are rendered. The pixels in the overlapping area are cleared. |
Destination-over (DST_OVER) |
If pixels in the source and the destination overlap, only the source pixels outside of the overlapping area are rendered. The pixels in the overlapping area are not changed. |
Destination-in (DST_IN) |
If pixels in the source and the destination overlap, the alpha from the source is applied to the destination pixels in the overlapping area. If the alpha = 1.0, the pixels in the overlapping area are unchanged; if the alpha is 0.0, pixels in the overlapping area are cleared. |
Destination-out (DST_OUT) |
If pixels in the source and the destination overlap, the alpha from the source is applied to the destination pixels in the overlapping area. If the alpha = 1.0, the pixels in the overlapping area are cleared; if the alpha is 0.0, the pixels in the overlapping area are unchanged. |
Clear (CLEAR) |
If the pixels in the source and the destination overlap, the pixels in the overlapping area are cleared. |
To change the compositing style used by the
Graphics2D class, create an AlphaComposite object and pass it into the setComposite method.
Example: Composite
This program illustrates the effects of various compositing style and alpha combinations.
Note: If you don't see the applet running, you need to install at least the Java SE Development Kit (JDK) 7 release.
Composite.java
A new AlphaComposite object ac is constructed by calling AlphaComposite.getInstance and specifying the desired compositing rule.
AlphaComposite ac = AlphaComposite.getInstance(AlphaComposite.SRC);
When a different compositing rule or alpha value is selected, AlphaComposite.getInstance is called again, and the new AlphaComposite is assigned to ac. The selected alpha is applied in addition to the per-pixel alpha value and is passed as a second parameter to AlphaComposite.getInstance.
ac = AlphaComposite.getInstance(getRule(rule), alpha);
The composite attribute is modified by passing the AlphaComposite object to Graphics 2D setComposite. The objects are rendered into a BufferedImage and are later copied to the screen, so the composite attribute is set on the Graphics2D context for the BufferedImage:
BufferedImage buffImg = new BufferedImage(w, h,
BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
Graphics2D gbi = buffImg.createGraphics();
...
gbi.setComposite(ac);