T 2.70 Lack of, or inadequate, planning of partitioning and replication in Novell eDirectory
Partitioning and replicating the eDirectory directory service are important aspects when planning the use.
Partitioning is the process of distributing the directory data of the eDirectory among separate areas (partitions). Not every partitioning scheme can be implemented as desired, and the scheme must follow certain rules that are based on the logic of the hierarchical tree structure. On the one hand, the purpose of partitioning is to distribute the load of the directory system to several areas and, on the other hand, it can make a physical separation of the storage location of directory data - according to the locations of an organisation,or example - possible Moreover, partitions may also constitute administrative units of the directory system.
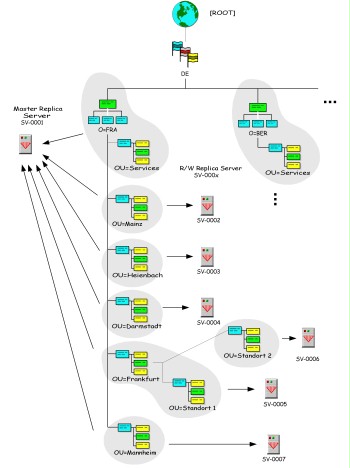
Figure: Example for a partitioned eDirectory directory service
The replication of partitions of the eDirectory primarily serves to increase the availability and to distribute the load of the directory system. Redundant data storage also improves the reliability.
For this reason, planning is particularly important, because it may be possible to subsequently change the partition and replication settings, but such changes may lead to inconsistencies under certain circumstances.
In the event of changes to the eDirectory, it naturally takes a certain time until the new settings have spread to all areas. This may result in a window which the eDirectory is inconsistent. Such inconsistencies may be a problem, particularly when defining the authentication data or regarding the data access rights to eDirectory objects, for example.
Partitioning the eDirectory directory has direct consequences for the inheritance of access rights (access control lists, ACL). In order to maintain the inheritance rules for an existing eDirectory tree, the root object of the new partition is informed about the superior ACL as inherited ACL by the system during partitioning.
The definition of the partitioning of the eDirectory service has direct effects on the replication activities of the overall system. In order to be able to efficiently search for objects in the entire tree (tree walking), the eDirectory automatically creates so-called subordinate reference replicas mainly containing branch addresses. If the planning is inappropriate (e.g. the tree structure is too flat), very comprehensive replication rings are generated here. If a replication ring becomes too large, there is a certain likelihood of at least one eDirectory server of the ring momentarily not being available. In such a case, error and status messages are generated on all other eDirectory servers of the replication ring. This may lead to an increase in the time and effort required for the administration of a large portion of the directory tree.
Furthermore, incorrect or inadequate planning of the partitions and replication of the directory service may also lead to losses of data, as well as to inconsistencies in the data storage, to poor availability of the directory service, to lower overall system performance, and possibly even to system failures.

