T 5.114 Misuse of spanning tree
The spanning tree protocol is specified in IEEE 802.1d. Spanning tree is used to prevent the formation of loops within a network comprising several switches. With this variant, redundant network structures are identified and a loop-free structure is formed. This measure reduces the active connection paths on any meshed network structure to a tree structure.
In the following illustration it can be seen that a port on the bottom switch has been disabled with the aid of spanning tree. By sending out Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs), a root bridge is identified based on the priority set and MAC address of the switch. In the illustration the switch at the top right is the root bridge.
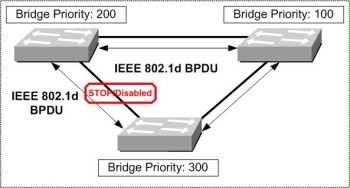
Figure: Spanning Tree
Spanning tree does not provide any authentication on the exchange of BPDUs. This situation can be exploited by attackers in switched networks. If an attacker can send BPDUs from a station connected to a switch, the topology will be recalculated with the aid of the spanning tree algorithm. The convergence for the calculation of the topology change can be 30 seconds with spanning tree. In this way, the availability of the network can be seriously affected by sending BPDUs.

