S 2.8 Assignment of access rights
Initiation responsibility: IT Security Officer, Head of IT
Implementation responsibility: Administrator, Specialists Responsible
Data access rights are used to regulate who is authorised within the framework of their function to use IT applications or data. The data access rights (e.g. read, write and execute) for IT applications, parts of applications or data depend on the function assumed by the person (e.g. application support, work preparation, system programming, application development, system administration, auditing, data acquisition, data processing). When granting data access rights, only access rights necessary to perform the corresponding tasks should be granted ("need-to-know" principle). The data access rights must be implemented by the rights administration of the IT system.
A number of IT systems allow you to define different rights as group rights or rights profiles (e.g. the Data Acquisition group). This definition corresponds to the technical implementation of the rights assigned to a given role or function. Creating such groups or profiles makes rights administration on an IT system easier since it can make assigning and changing these rights much simpler.
The specification of the data access rights and any changes to them must be performed and documented by the corresponding person responsible. The documentation must contain the following information:
- Which roles and functions have been granted which data access rights (taking the separation of functions principle into account, see S 2.5 Division of responsibilities and separation of functions),
- Which groups and/or profiles have been set up,
- Who fulfils which functions,
- Which data access rights a person will have in the context of which roles (the data access rights of substitutes also need to be documented),
- Which conflicts arose while granting the (application/data) access authorisations. These conflicts can arise because, for example, someone fulfils incompatible functions or it is impossible on some IT systems to separate certain data access rights.
- Who will be granted which data access rights in an emergency, for example because they are a member of the crisis team.
The procedure for separating functions and assigning access rights is illustrated in the following example.
The application examined is a travel expense accounting system. The relevant rooms are shown in the following diagram. The IT system consists of a LAN to which three PCs, a server and the operating console are connected.
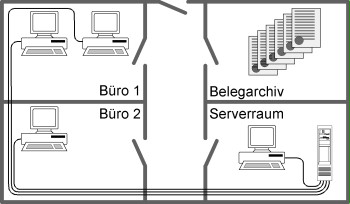
Figure: Division of responsibilities and separation of functions
Step 1: Division of responsibilities and separation of functions
The following functions are required for the travel expense accounting system examined:
- LAN administration
- Audit Department
- Data acquisition
- Processing, including verification of the mathematical accuracy
- Processing, including verification of the factual accuracy
- Processing, including the authority to order payment
The following functions are not compatible with each other due to inherent constraints:
- Function 1 and Function 2 (the administration is not allowed to audit itself)
- Function 2 and Function 6 (the person authorised to order payment is not allowed to audit themself)
- A combination of Functions 4 or 5 with Function 6 (the two-person rule would be violated in the case of payment orders)
These functions are fulfilled by the following people:
| Mr. Mayer | Ms. Schmidt | Mr. Mueller | Ms. Fleiss | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN administration | X | |||
| 2. | Audit Department | X | |||
| 3. | Data acquisition | X | |||
| 4. | Processing, mathematical accuracy | X | |||
| 5. | Processing, factual accuracy | X | |||
| 6. | Authority to order payment | X |
Step 2: Assignment of site access rights
The following provides reasons for the given protection requirement of each type of room and documents the assignments of the site access rights in the table:
- Server room:
Unauthorised access to the server must be prevented because the availability, integrity, and confidentiality of the entire application depend on this central component. - Document archive:
For accounting purposes, the travel expense reports need to be stored for longer periods of time. It must be ensured that the documents are stored unchanged and in their entirety.- Office 1
In this office, the data needed is acquired and the mathematical and factual accuracy is checked. To guarantee the correctness of these processes, unauthorised access to the workstation computers must be prevented. - Office 2
Payment orders for the travel expenses are issued on the PC in this office. This process may only be performed by authorised persons. Unauthorised persons must be denied access.
- Office 1
| Server room | Document archive | Office 1 | Office 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN administration | X | |||
| 2. | Audit Department | X | X | X | X |
| 3. | Data acquisition | X | |||
| 4. | Processing, mathematical accuracy | X | X | ||
| 5. | Processing, factual accuracy | X | X | ||
| 6. | Authority to order payment | X | X | X |
Step 3: Granting of (system/network) access authorisations
The following access authorisations result for the functions:
| Operating system server | Application log evaluation | Application data acquisition | Application document processing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN administration | X | |||
| 2. | Audit Department | X | X | X | |
| 3. | Data acquisition | X | |||
| 4. | Processing, mathematical accuracy | X | |||
| 5. | Processing, factual accuracy | X | |||
| 6. | Authority to order payment | X |
Step 4: Granting of (application/data) access authorisations
In the following, the data access rights needed to fulfil a function are shown. Legend:
- E = Right to the execute the application/software
- R = Read privilege for data
- W = Write privilege, i.e. to create data
- M = Right to modify data
- D = Right to delete data
- S = Right to sign payment orders
| Operating system server | Log evaluation | Application data acquisition | Application document processing | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | LAN administration | E,R,W,M,D | |||
| 2. | Audit Department | E,L | E,R,D | E,L | |
| 3. | Data acquisition | E,W | |||
| 4. | Processing, mathematical accuracy | E,R,M | |||
| 5. | Processing, factual accuracy | E,R,M | |||
| 6. | Authority to order payment | E,R,S |
Such documentation makes it easier to allocate the rights. Assuming that Ms. Schmidt changes companies and her position needs to be filled, then it is easy to determine which of Ms. Schmidt's former rights need to be deleted and assigned to the new employee based on the tables above. If the new employee should also work as a substitute in processing and be allowed to order payments in this function, then the conflict arising from the fact that the new employee would be able to make changes without being detected when acting as a substitute becomes apparent when examining which rights the new employee would need to be granted.
Review questions:
- Is up-to-date documentation on the data access rights granted available?
- Have only those data access rights been granted that are needed to perform the particular tasks?
- Are data access right requests and changes to existing data access rights checked and approved by the person responsible for this?
- Is there a controlled procedure for withdrawing data access rights?

