S 2.344 Secure operation of SAP systems on the Internet
Initiation responsibility: Head of IT, Head of Development, IT Security Officer
Implementation responsibility: Developer, Administrator
SAP systems are being used more and more often in Internet scenarios. In this case, the corresponding additional applications are generally installed or they are used as backend systems within the framework of Internet portal scenarios (see also S 2.343 Protection of SAP systems in a portal scenario). Access in Internet scenarios is generally obtained using HTTP and users obtain access through a browser.
For this reason, the following aspects must be taken into consideration in Internet scenarios:
Restricting system access after a risk analysis
All SAP systems that will be accessed directly from the Internet are subject to greater risk. This must be taken into account when performing the risk analysis. Access to the SAP systems concerned must be restricted by a firewall to the ports used to process HTTP and/or HTTPS requests only.
In general, the same requirements apply to accesses to a SAP system from the Internet as for any other system, for example a web server (see also module S 5.4 Web servers). For this reason, the general safeguards relevant to networked systems connected to the Internet must be taken into consideration. For example, it may make sense to access the SAP system through a reverse proxy or an application firewall (see also module S 3.1 Security gateway (firewall)).
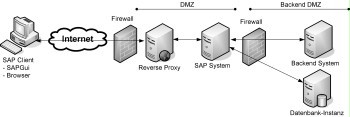
Figure: SAP system in the Internet
Checking and securing communication interfaces
Applications are provided using the HTTP-based interfaces. A risk analysis must be performed both for the system applications and for normal applications. Furthermore, it makes sense to conduct a security check of the web interface so it is possible to estimate the threats posed by typical web-based attacks.
In general, it must be noted that RFC access can also be obtained using the HTTP interface. For this reason, only those services should be enabled that are actually needed and whose suitability for operation in the Internet has been examined carefully.
Restricting dialogue accesses
Direct SAPGui access to the SAP systems using the Internet should be prohibited, and access should be restricted by a firewall to the HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
Internet Transaction Server
If the Internet Transaction Server (ITS) is not used to access the SAP system, ITS access should be disabled, since it offers access to the SAP system that is similar to SAPgui access.
An ITS component needs to be installed as a separate component (WGate, AGate) when using version 6.40 or older versions of the SAP Web Application Server. In this case, these components should not be installed. Version 6.40 and higher integrate the IST so that the corresponding services need to be disabled in the ABAP stack (e.g. Webgui, see S 5.127 Protection of the SAP Internet Connection Framework (ICF)) and Java stack (e.g. mi or me, see S 4.266 Secure configuration of the SAP Java Stack).
If ITS is used, it is necessary to carefully examine the authorisations in the SAP system as to whether only the allowed functions can actually be called. Spot checks are not adequate in this case. The examination will take significant time and effort under some circumstances. In particular, all transactions that do not need to be accessed should be disabled in order to ensure that they cannot be called due to critical combinations of authorisations. Since an SAP system may contain several thousand transactions, this configuration process takes a lot of time and so it is generally impossible to perform. For this reason, this risk must be kept to a minimum through a carefully planned authorisation concept.
Authentication/single sign-on
Single sign-on accesses from the Internet should only be enabled between the systems approved for Internet access.
No trust relationships should be configured for external systems, since it is impossible to control the security of the external systems.
Authorisations
It must be ensured that the authorisations of the users maintained in the SAP system are specified so that they are only granted the minimum authorisations necessary. It is recommended to use accounts of type Communication or Internet User for users who do not need SAPgui access.
Validating data from SAP systems with Internet access
Data passed from SAP systems with Internet access to systems without Internet access - for example through requests or data transports - must be validated before it is passed on to the backend system.
Available data
If data from internal SAP systems will be made available on SAP systems with Internet access, the following should be checked:
- It should be checked whether it is really necessary to provide the data by directly accessing the internal systems or whether periodic data exports and imports can be used. This prevents access to the internal systems from the outside.
- When exporting data, it should be examined whether all information must be exported or whether only some of the information is actually needed. This limits the amount of data stored on the SAP systems with Internet access.
When using an import/export solution, it must be taken into account that such solutions prevent direct integration of the application (for example for CRM or SRM systems) so that the advantages of direct integration cannot be utilised any more. In addition, the data transport needs to be configured and administrated in this case. For this reason, this solution should only be used in general for simple scenarios.
Review questions:
- Have SAP systems directly called from the Internet been taken into consideration during risk analysis?
- When using ITS, is it checked whether only the admissible functions can be called in each case?
- Has it been ensured that single sign-on access from the Internet is only enabled between the systems approved for Internet access in the SAP system?
- Has it been ensured that no trust relationships are configured for external systems in the SAP system?
- Is the data passed from SAP systems with Internet access to systems without Internet access validated before it is passed on to the backend system?
- When exporting data, is it verified that only the required part of the information is exported?

